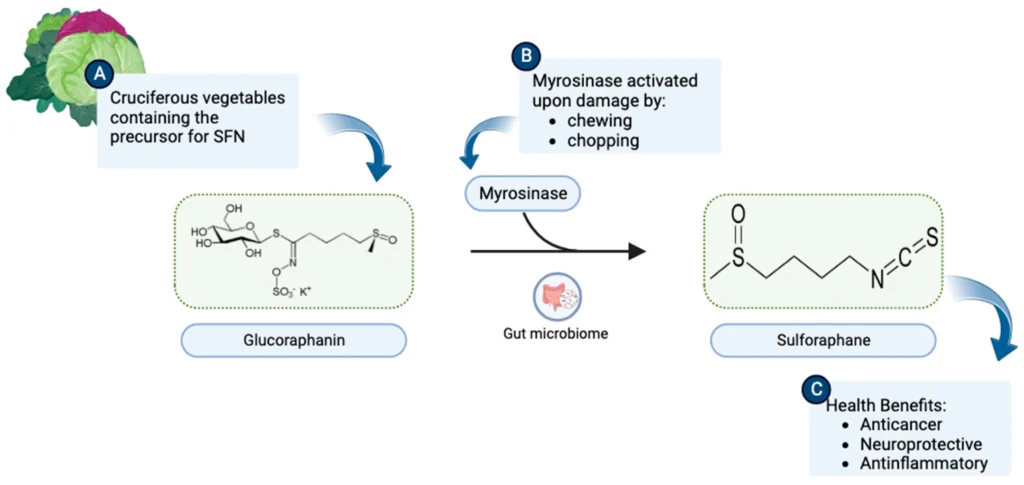
Tutti abbiamo sentito dire che i broccoli sono un "superfood". Per decenni è stato elogiato per i suoi impressionanti benefici per la salute. Ma vi siete mai chiesti cosa conferisce a questo umile ortaggio il suo potere? Il segreto non è un solo composto, ma una straordinaria collaborazione naturale. Al centro c'è una molecola stabile chiamata glucorafanina.

Pensate a glucorafanina come la chiave che sblocca il pieno potenziale del composto più famoso dei broccoli, sulforafano. Sebbene il sulforafano riceva la maggior parte del credito, ottenerlo direttamente è difficile. Questo articolo ne analizza i motivi concentrandosi sul suo precursore, glucorafaninaè una strategia più intelligente ed efficace per sfruttare i profondi benefici per la salute nascosti nelle verdure crucifere.
Che cos'è esattamente la glucorafanina?
In parole povere, glucorafanina è un composto altamente stabile, presente in natura, che si trova in abbondanza nelle verdure crucifere come broccoli, cavoli e cavolfiori. Appartiene a una famiglia di composti chiamati glucosinolati.
Immaginatelo come un pacchetto energetico sigillato e protetto. Da solo, i suoi effetti sono modesti. Ma quando viene attivato, si trasforma in uno dei più potenti composti naturali per la salute conosciuti dalla scienza: sulforafano. Questa trasformazione è la fonte della sua potenza, che rende glucorafanina il punto di partenza essenziale per una cascata di benefici cellulari. Il suo ruolo principale nella pianta è quello di fungere da meccanismo di difesa, pronto a scatenarsi quando la pianta viene danneggiata.
La conversione magica: Come la glucorafanina diventa sulforafano
La trasformazione di glucorafanina in sulforafano non è una semplice reazione chimica, ma una brillante opera di ingegneria naturale. Il processo richiede un enzima specifico che funge da catalizzatore.
L'attore chiave: L'enzima mirosinasi
Il segreto di questa conversione è un enzima chiamato mirosinasi. In una pianta sana e intatta, glucorafanina e mirosinasi sono conservati in compartimenti separati all'interno delle cellule della pianta. Sono come una resina epossidica a due componenti; solo quando si mescolano creano qualcosa di potente.
Quando si tritano, si masticano o si frullano le crucifere, si rompono le pareti cellulari, consentendo di mirosinasi entrare in contatto con glucorafanina. Questa interazione innesca istantaneamente la conversione, producendo l'altamente bioattivo sulforafano proprio quando ne avete bisogno. Anche i batteri intestinali possono effettuare una conversione simile, assicurando ulteriormente i benefici.
Perché questo processo in due fasi è importante per la vostra salute
Questo processo naturale in due fasi è incredibilmente efficiente. Assicura che l'altamente reattivo sulforafano viene generato al momento del consumo, massimizzando la sua freschezza e potenza. Questo elegante sistema evidenzia perché la stabilità di glucorafanina è così cruciale: conserva il potenziale fino all'ultimo secondo.
Il processo di conversione: Glucorafanina (precursore stabile) + Mirosinasi (attivatore) → Sulforafano (potente attivatore)
I 5 principali benefici della glucorafanina, comprovati dalla scienza
I benefici per la salute di glucorafanina sono realizzati attraverso la sua conversione in sulforafanoche è uno dei più potenti attivatori naturali conosciuti di un percorso cellulare chiamato NRF2. Questa via è il regolatore principale dei sistemi antiossidanti e di disintossicazione dell'organismo.
1. Un maestro antiossidante e disintossicante
Il sulforafano attiva potentemente la via NRF2, attivando oltre 200 geni antiossidanti e di disintossicazione. Questo non si limita a neutralizzare i radicali liberi, ma potenzia la capacità dell'organismo di proteggersi dallo stress ossidativo e di eliminare le tossine nocive, favorendo la funzionalità epatica e la salute cellulare in generale.
2. Un potente agente antinfiammatorio
L'infiammazione cronica è la causa principale di molte malattie moderne. Il sulforafano aiuta a combattere questo fenomeno inibendo le molecole pro-infiammatorie come NF-kB. Calmando l'infiammazione a livello cellulare, glucorafanina può contribuire alla salute delle articolazioni, al benessere cardiovascolare e a una risposta immunitaria equilibrata.
3. Supporta la salute del cervello e la funzione cognitiva
Il cervello è altamente suscettibile allo stress ossidativo. Attivando l'NRF2 nelle cellule cerebrali, il sulforafano fornisce una potente neuroprotezione. Alcuni studi, tra cui quelli della Johns Hopkins University, hanno esplorato il suo potenziale nel supportare le funzioni cognitive, nel proteggere dal declino legato all'età e persino nel riequilibrare i processi cellulari in aree come il disturbo dello spettro autistico (ASD).
4. Promuove la salute della pelle e la protezione dai raggi UV
La pelle è la prima linea di difesa contro i fattori di stress ambientale, compresi i raggi UV. Il sulforafano aiuta a proteggere le cellule della pelle dai danni del sole dall'interno, attivando i meccanismi di difesa della pelle stessa. Ciò può contribuire a ridurre il rossore e l'infiammazione associati all'esposizione ai raggi UV e a favorire un colorito più resistente e giovane.
5. Può offrire protezione cellulare
Una delle aree più studiate del sulforafano è il suo ruolo nella salute cellulare. Sostiene i processi naturali dell'organismo per l'eliminazione delle cellule danneggiate e inibisce le vie che possono portare alla crescita di cellule anomale. Pur non essendo un trattamento, una dieta ricca di glucorafanina è una pietra miliare di uno stile di vita proattivo e protettivo per le cellule.
Glucorafanina e sulforafano: qual è la scelta migliore?
Con l'aumento degli integratori, è emersa una domanda fondamentale: è meglio assumere glucorafanina o sulforafano direttamente? La scienza indica che glucorafanina come scelta più intelligente.
Il vantaggio della stabilità della glucorafanina
Sulforafano è una molecola incredibilmente reattiva e instabile. Si degrada rapidamente, rendendo difficile la cattura e la stabilizzazione in un integratore. Glucorafaninaè invece eccezionalmente stabile. Può essere facilmente estratto, standardizzato e fornito in un integratore, garantendo una dose costante e potente ogni volta.
Biodisponibilità e assorbimento
Quando si consuma glucorafanina insieme al mirosinasi Il corpo gestisce naturalmente la conversione, garantendo un assorbimento ottimale. Alta qualità glucorafanina Gli integratori spesso includono mirosinasi per garantire che questa conversione avvenga in modo efficiente all'interno dell'apparato digerente.
Tabella di confronto
| Caratteristica | Glucorafanina | Sulforafano |
|---|---|---|
| Stabilità | Molto alto (molecola stabile) | Molto basso (altamente reattivo) |
| Forma | Precursore (necessita di attivazione) | Composto attivo |
| Integrazione | Facile da standardizzare e consegnare | Difficile da stabilizzare e verificare |
| Meccanismo | Convertito nell'organismo secondo le necessità | Immediatamente attivo, ma si degrada rapidamente |
| Il verdetto | La scelta più intelligente e affidabile | Meno pratico per un dosaggio costante |
Come ottenere la glucorafanina: Alimenti e integratori
Potete aumentare il vostro glucorafanina attraverso la dieta e l'integrazione.
Le fonti alimentari più ricche
Senza dubbio, la più potente fonte alimentare di glucorafanina è germogli di broccoli. Queste minuscole piante, di 3-5 giorni, contengono da 10 a 100 volte di più glucorafanina in peso rispetto ai broccoli maturi. Altre buone fonti sono:
- Broccoli maturi (soprattutto le cimette)
- Cavolfiore
- Cavolo
- Cavoletti di Bruxelles
- Cavolo
Consigli per massimizzare la glucorafanina dalla dieta
La cottura può disattivare il mirosinasi enzima. Per ottenere il massimo beneficio:
- Mangiare crudo: Aggiungete i germogli di broccoli alle insalate e ai panini.
- Vapore leggero: Cuocere i broccoli a vapore per non più di 1-3 minuti.
- "Hack and Hold": Tritare i broccoli e lasciarli riposare per 40 minuti prima della cottura. Questo permette di iniziare la conversione prima che il calore disattivi l'enzima.
- Aggiungere un amplificatore: Abbinate alle verdure crucifere cotte una fonte cruda di mirosinasi, come una spolverata di semi di senape in polvere.
Quando prendere in considerazione un integratore di glucorafanina
Sebbene una dieta sana sia essenziale, può essere difficile assumere una dose costante e terapeutica di glucorafanina quotidiano. Un prodotto di alta qualità glucorafanina L'integratore offre un modo affidabile per garantire l'assunzione di una quantità standardizzata, spesso abbinata al necessario mirosinasi enzima per garantire l'attivazione.
Dosaggio, sicurezza e potenziali effetti collaterali
Glucorafanina è generalmente riconosciuto come sicuro (GRAS). Negli studi clinici, i dosaggi variano in genere da 15 a 60 mg al giorno, che corrispondono a circa 100-400 mg di estratto standardizzato di germogli di broccoli.
Gli effetti collaterali sono rari e di solito lievi, come gas o disturbi digestivi, soprattutto a dosi elevate. Come per qualsiasi altro integratore, è meglio consultare un professionista del settore sanitario prima di iniziare, soprattutto in caso di gravidanza, allattamento o patologie.
Conclusione: La chiave per sbloccare il potere delle crucifere
Glucorafanina è più di un semplice composto; è l'elegante sistema di somministrazione della natura per i potenti benefici di sulforafano. Agendo come precursore stabile e affidabile, garantisce che l'organismo riceva tutto il potenziale protettivo delle verdure crucifere.
Sia che si scelga di riempire il piatto di germogli di broccoli o che si opti per la comodità di un integratore di alta qualità, concentrarsi su glucorafanina è una strategia scientificamente fondata per potenziare le difese antiossidanti dell'organismo, calmare le infiammazioni e sostenere la salute cellulare a lungo termine. È davvero la chiave per svelare uno dei segreti più potenti della natura.
Domande frequenti (FAQ)
D1: Assumere glucorafanina equivale a mangiare broccoli?
Sebbene mangiare broccoli sia altamente benefico per le sue fibre e gli altri nutrienti, un integratore può fornire una dose molto più elevata e consistente di glucorafanina rispetto a quello che si ottiene in genere con la sola dieta, soprattutto se i broccoli sono cotti.
D2: Perché la mirosinasi è così importante per la glucorafanina?
La mirosinasi è l'enzima che "attiva" glucorafaninaconvertendolo nella sostanza bioattiva sulforafano. Senza di essa, la conversione è molto meno efficiente e non si ottengono tutti i benefici per la salute.
D3: Posso assumere una quantità sufficiente di glucorafanina solo dagli alimenti?
Per il benessere generale, una dieta ricca di verdure crucifere è eccellente. Tuttavia, per una dose terapeutica finalizzata a specifici obiettivi di salute, può essere impegnativa. Per esempio, è necessario mangiare più di mezzo chilo di broccoli maturi per ottenere la stessa quantità di glucorafanina che si trova in una piccola porzione di germogli di broccoli o in una singola capsula di integratore.
D4: Qual è la differenza tra gli integratori di glucorafanina e di sulforafano stabilizzato?
Glucorafanina Gli integratori forniscono il precursore stabile, affidando all'organismo (con l'aiuto della mirosinasi) la conversione. "Stabilizzato" sulforafano Gli integratori cercano di fornire direttamente il composto attivo, ma la sua instabilità intrinseca rende difficile garantire potenza ed efficacia.
D5: Ci sono effetti collaterali dell'assunzione di glucorafanina?
Glucorafanina è molto ben tollerato. L'effetto collaterale più comune, anche se raro, è un lieve disturbo digestivo o gas, che spesso si attenua con l'adattamento dell'organismo.