Se mergulhou no mundo da saúde e do bem-estar ultimamente, provavelmente já viu proteína de ervilha em todo o lado. Está nos batidos, nas barras de proteínas e até nos hambúrgueres à base de plantas. Mas uma pergunta incómoda impede muitas vezes as pessoas de a adoptarem totalmente: A proteína de ervilha é uma completo proteína?
A resposta curta é, para todos os efeitos práticos, sim. Mas a história completa é um pouco mais matizada e, francamente, muito mais interessante. Acredito que compreender o "porquê" por detrás do produto é a chave para libertar todo o seu potencial para os seus objectivos de saúde.
Este guia irá guiá-lo por tudo o que precisa de saber. Vamos desmontar os mitos, analisar a ciência por detrás do seu poder de construção muscular e mostrar-lhe exatamente como se compara com outras proteínas.
O que é exatamente a proteína de ervilha?
Antes de entrarmos nos pormenores dos aminoácidos, comecemos pelo básico. O que é isto?
Da ervilha amarela ao pó: Uma análise simples
Como deve calcular, a proteína de ervilha provém de ervilhas - especificamente, ervilhas amarelas. No entanto, não é tão simples como moer um saco de ervilhas. O processo envolve secar e moer as ervilhas até obter uma farinha fina. Esta farinha é depois misturada com água para separar a proteína da fibra e do amido. O resultado é uma proteína em pó limpa e concentrada.
Normalmente, é vendido sob algumas formas:
- Isolado de proteína de ervilha: A forma mais comum, contendo cerca de 90% de proteínas. A maior parte dos hidratos de carbono e das fibras foram retirados.
- Concentrado de proteínas de ervilha: Contém um pouco menos de proteínas (75-80%) e retém mais fibras naturais e hidratos de carbono.
- Proteína texturizada de ervilha: Muitas vezes utilizado como substituto da carne em alimentos como hambúrgueres à base de plantas.
Para efeitos de um batido de proteínas, o mais provável é utilizar a proteína isolada.
A grande questão: Será que Proteína de ervilha uma proteína "completa"?
Muito bem, vamos lá abordar o assunto principal. Esta pergunta é provavelmente a principal razão pela qual estão aqui. Para a responder, precisamos primeiro de concordar com o significado de "completo".
Primeiro, o que é que torna uma proteína "completa"?
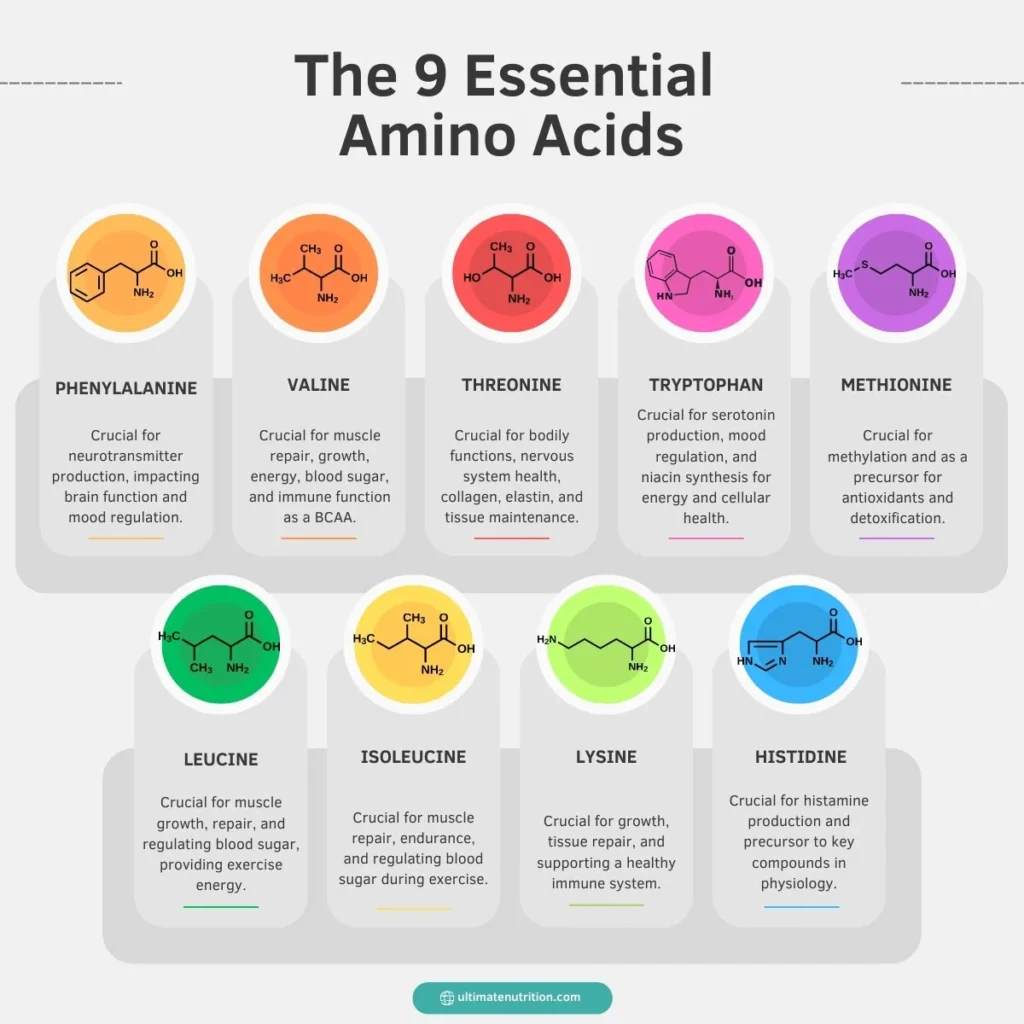
Pense nas proteínas como uma casa. Para construir essa casa, são necessários diferentes tipos de tijolos. No teu corpo, estes "tijolos" são chamados aminoácidos. Existem 20 aminoácidos diferentes que o seu corpo utiliza para construir tudo, desde tecido muscular a enzimas e hormonas.
Destes 20, nove são considerados aminoácidos essenciais (EAA). São "essenciais" porque o nosso corpo não consegue produzi-los por si só. deve obtê-los a partir dos alimentos. Uma fonte alimentar é considerada uma "proteína completa" se contiver todos os nove aminoácidos essenciais em quantidades aproximadamente suficientes. As proteínas animais como a carne, os ovos e os lacticínios são exemplos clássicos.
O perfil de aminoácidos da proteína de ervilha
Então, qual é a posição da proteína de ervilha? Aqui está o facto crucial: A proteína de ervilha contém todos os nove aminoácidos essenciais.
É aqui que começa frequentemente a confusão. Tecnicamente, para ser "completa" segundo a definição mais rigorosa, uma proteína precisa de ter níveis elevados de todos os nove EAAs. A proteína de ervilha é fantástica em quase todos eles, especialmente nos aminoácidos de cadeia ramificada (BCAAs), que fortalecem os músculos. No entanto, é ligeiramente baixa num EAA: metionina.
Porque é que é "funcionalmente completo" para o seu corpo
Será que esta ligeira diminuição da metionina é realmente importante? Para a grande maioria de nós, a resposta é um retumbante não. Este é um caso clássico em que nos perdemos nas ervas daninhas da nutrição e não percebemos o panorama geral. Descobri que as pessoas se fixam frequentemente neste único pormenor, sem considerar a forma como realmente comemos.
Pense na sua dieta como um todo. Não se consome apenas proteína de ervilha isoladamente durante dias a fio. A "lacuna" de metionina é incrivelmente fácil de preencher com outros alimentos comuns que provavelmente já está a comer. Alimentos como arroz, aveia, nozes e pão integral são ricos em metionina.
Por isso, se tomar um batido de proteína de ervilha ao pequeno-almoço e uma sanduíche em pão integral ao almoço, já cobriu todas as suas necessidades. O seu corpo é inteligente; acumula aminoácidos de diferentes refeições ao longo do dia. É por isso que muitos especialistas em nutrição preferem atualmente o termo "proteínas complementares" a obsessão pela plenitude de um único alimento.
Para todos os efeitos, a proteína de ervilha é uma fonte de proteína funcionalmente completa e incrivelmente eficaz.
Para além da proteína: Todo o poder nutricional da proteína de ervilha
O que é verdadeiramente excitante na proteína de ervilha é o facto de os seus benefícios não se limitarem ao seu perfil de aminoácidos. É uma potência nutricional também noutros aspectos.
- Rico em ferro: Uma única dose pode fornecer uma porção significativa das suas necessidades diárias de ferro, o que é uma grande vantagem, especialmente para quem segue uma dieta à base de plantas.
- Repleto de BCAAs: É particularmente rico em leucina, isoleucina e valina - os três BCAAs famosos por impulsionar a reparação e o crescimento muscular.
- Alto teor de arginina: Este aminoácido promove um fluxo sanguíneo saudável, o que é ótimo tanto para a saúde do coração como para o desempenho atlético.
- Limpo e magro: É naturalmente sem leite, sem soja, sem glúten e com baixo teor de hidratos de carbono, o que o torna adequado para quase todos os planos alimentares.
Os 5 principais benefícios científicos da proteína de ervilha
- Constrói músculos tão eficazmente como o Whey Este pode ser o benefício mais surpreendente para alguns. Um estudo de referência de 2015 publicado na revista Jornal da Sociedade Internacional de Nutrição Desportiva descobriram que os atletas que tomaram suplemento com proteína de ervilha obtiveram os mesmos ganhos musculares que os que usaram proteína de soro de leite. O motivo? O seu conteúdo de BCAA de alta qualidade dá aos músculos o combustível exato de que necessitam para recuperar.
- Apoia a gestão do peso, mantendo-o saciado A proteína é bem conhecida pela sua capacidade de promover a saciedade (a sensação de plenitude). Alguns estudos sugerem que a proteína de ervilha pode ser ainda mais eficaz do que outras proteínas para controlar a fome, ajudando-o a reduzir a ingestão total de calorias sem se sentir privado.
- Bom para a saúde do coração Não é apenas para os seus músculos. A investigação indicou que a proteína de ervilha pode ajudar a baixar a tensão arterial elevada e a reduzir os níveis de colesterol, tornando-a uma escolha inteligente para o coração.
- Uma potência anti-alérgica Para quem sofre de sensibilidade aos lacticínios, à lactose, à soja ou ao glúten, a proteína de ervilha é um divisor de águas. Fornece proteínas de alta qualidade sem o inchaço, gases ou reacções alérgicas normalmente associados a outras proteínas em pó. É uma opção suave mas poderosa.
- Rico em ferro A deficiência de ferro é uma preocupação comum, particularmente para mulheres e veganos. A proteína de ervilha oferece uma fonte fantástica à base de plantas deste mineral essencial, que é vital para transportar oxigénio no sangue e manter os níveis de energia.
Existem desvantagens? Um olhar transparente sobre os efeitos secundários
Nenhum alimento é perfeito, e é importante ser honesto sobre os potenciais inconvenientes. Felizmente, os problemas com a proteína de ervilha são menores e muitas vezes evitáveis.
- Potencial de inchaço e gases: Algumas pessoas sentem um ligeiro inchaço, especialmente quando o experimentam pela primeira vez. Isto deve-se frequentemente ao facto de os "concentrados" de qualidade inferior conterem mais fibras. Solução: Opte por uma proteína de ervilha "isolada" de alta qualidade, que é mais refinada, e não se esqueça de beber muita água.
- A preocupação com os metais pesados: Esta é uma preocupação legítima para muitos alimentos à base de plantas, não apenas para a proteína de ervilha. As plantas podem absorver quantidades vestigiais de metais pesados (como o chumbo e o cádmio) do solo. Solução: É aqui que a reputação da marca se torna crítica. Escolha uma marca de confiança que efectue testes de metais pesados por terceiros e seja transparente com os seus resultados.
- Sabor e textura: Sejamos realistas, a proteína de ervilha sem sabor pode ter um sabor distinto a "terra" e uma textura ligeiramente arenosa. Mas eu vejo isto como uma tela em branco! Mistura-se lindamente em batidos com fruta, cacau em pó ou uma pitada de canela.
Proteína de ervilha vs. outras proteínas populares: Uma Comparação Cabeça a Cabeça
| Caraterística | Proteína de ervilha | Proteína de soro de leite | Proteína de soja |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qualidade das proteínas | Funcionalmente completo | Completo | Completo |
| Construção muscular | Excelente (elevado teor de BCAAs) | Excelente (elevado teor de BCAAs) | ✅ Bom |
| Amigo das alergias | Excelente (hipoalergénico) | Contém lacticínios/lactose | Alergénio comum |
| Digestibilidade | Geralmente fácil | Pode causar inchaço | Pode causar problemas a algumas pessoas |
| Sustentabilidade | Excelente (baixo consumo de água/terra) | ❌ Moderado | discutível (desflorestação) |
| Melhor para | Veganos, pessoas alérgicas | Qualquer pessoa sem alergias | Vegans que pretendem um perfil completo |
Como escolher a melhor proteína em pó de ervilha (e como usá-la)
Navegar no corredor dos suplementos pode ser avassalador. Eis o que deve procurar no rótulo:
- Isolado de proteína de ervilha: Para um teor de proteínas mais elevado e uma digestão mais suave.
- Orgânico e não OGM: Assegura que as ervilhas foram cultivadas sem pesticidas sintéticos.
- Testado por terceiros: Isto não é negociável. É a sua garantia de pureza e segurança.
- ✅ Ingredientes mínimos: Os melhores pós contêm apenas um ingrediente: proteína isolada de ervilha. Evite produtos com uma longa lista de adoçantes artificiais, enchimentos e gomas.
Quando se tem um ótimo pó, as possibilidades são infinitas. As minhas formas preferidas de o utilizar são num batido pós-treino com banana e leite de amêndoa, misturado nas minhas papas de aveia matinais, ou mesmo misturado na massa de panquecas para um pequeno-almoço repleto de proteínas.
Conclusão: O seu veredito sobre a proteína de ervilha
Então, vamos voltar à nossa pergunta original. A proteína de ervilha é uma proteína completa? Embora possa ser tecnicamente pobre num aminoácido, é uma fonte de nutrição que é, para todos os efeitos funcionais, completa e incrivelmente eficaz.
Constrói músculos como o soro de leite, apoia a saúde do coração e é um porto seguro para qualquer pessoa com sensibilidades alimentares. Os desafios - como o sabor ou potenciais contaminantes - são facilmente resolvidos escolhendo um produto de alta qualidade e sendo um pouco criativo na cozinha.
Para quem procura uma proteína de origem vegetal limpa, sustentável e poderosa, o veredito está dado: a proteína de ervilha é uma vitória retumbante.
Perguntas frequentes (FAQ)
A proteína de ervilha é uma proteína completa?
Sim, contém todos os nove aminoácidos essenciais. Embora ligeiramente pobre em metionina, este facto é facilmente compensado por uma dieta equilibrada, tornando-a "funcionalmente completa".
A proteína de ervilha é melhor do que a de soro de leite?
"Melhor" depende dos seus objectivos. Para a construção muscular, são igualmente eficazes. Se tem alergia aos lacticínios ou é vegan, a proteína de ervilha é a clara vencedora.
A proteína de ervilha pode ajudar a construir músculo?
Sem dúvida. Estudos científicos demonstraram que estimula o crescimento muscular de forma tão eficaz como a proteína de soro de leite, graças ao seu elevado teor de BCAA.
A proteína de ervilha provoca inchaço ou gases?
Pode acontecer com alguns, especialmente com concentrados de qualidade inferior. A escolha de uma proteína isolada de ervilha de elevada pureza e a ingestão de água suficiente evitam normalmente este problema.
É seguro consumir proteína de ervilha todos os dias?
Sim, para a maioria das pessoas, o consumo diário de proteína de ervilha como parte de uma dieta equilibrada é perfeitamente seguro e pode ser uma óptima forma de satisfazer as suas necessidades proteicas.
A proteína de ervilha contém metais pesados?
Todos os alimentos à base de plantas podem conter vestígios de metais pesados provenientes do solo. As marcas de renome efectuam testes por terceiros para garantir que os seus produtos são seguros e estão muito abaixo dos limites regulamentares. Escolha sempre uma marca em que confie.