If you’re trying to reduce your sugar intake, you’ve likely found yourself staring at a wall of colorful packets, wondering which artificial sweetener to choose. Two of the most common options are sucralose そして aspartame. They both promise sweetness without the calories, but the debate around them can be confusing. Is one safer? Does one taste better? Which is the right choice for your coffee, your baking, or your health goals?
Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered. This guide will cut through the noise and give you a clear, science-backed comparison. By the end, you’ll know exactly which sweetener is the right fit for you.
Quick Look: Sucralose vs. Aspartame at a Glance
For those in a hurry, here’s a quick side-by-side comparison of the key differences.
| 特徴 | Sucralose (e.g., Splenda) | Aspartame (e.g., Equal, NutraSweet) |
|---|---|---|
| 起源 | Chemically altered sucrose (sugar) | Made from two amino acids |
| 甘さ | ~600x sweeter than sugar | ~200x sweeter than sugar |
| カロリー | Zero | Zero |
| 熱安定性 | Stable at high temperatures | Breaks down with heat |
| 最適 | Baking, cooking, hot drinks | Cold drinks, yogurt, tabletop sweetener |
| 味覚プロフィール | Generally clean, some report a slight aftertaste | Closer to sugar, but can have a distinct aftertaste |
| Safety Consensus | Approved by FDA, WHO | Approved by FDA, WHO |
| Special Notes | Minimal absorption by the body | Not safe for people with PKU |
Understanding the Basics: What Are They?
Before we dive deeper, let’s get to know our contenders.
What Is Sucralose?
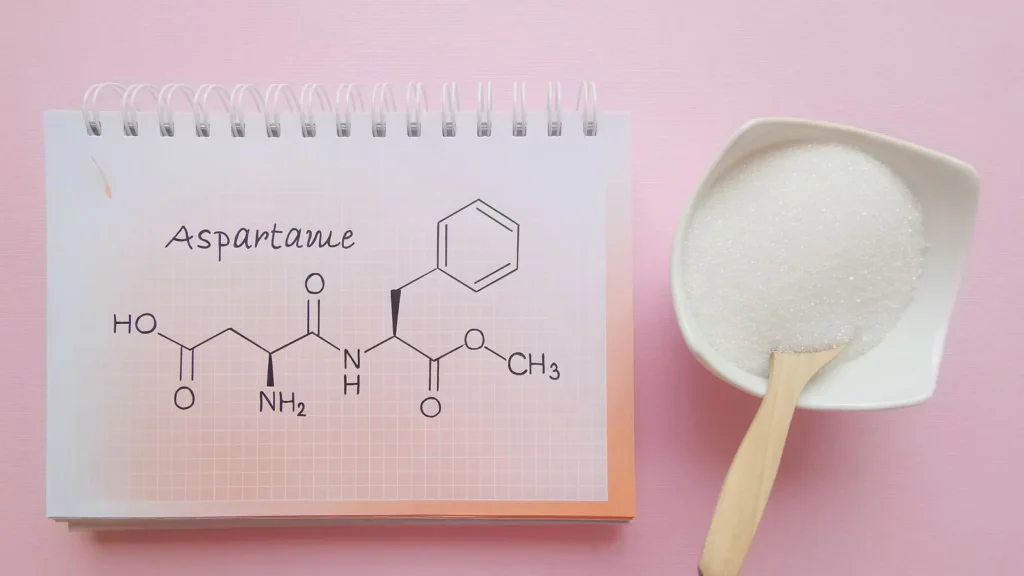
スクラロース is a zero-calorie artificial sweetener that is most commonly sold under the brand name Splenda. It’s unique because it’s actually made from real sugar. Through a chemical process, three hydrogen-oxygen groups on the sucrose molecule are replaced with chlorine atoms. This change makes it intensely sweet and prevents your body from metabolizing it, which is why it provides no calories.
What Is Aspartame?
Aspartame, known by brand names like Equal そして NutraSweet, is another popular zero-calorie sweetener. It’s created by bonding two amino acids: aspartic acid and phenylalanine. Since amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, you can find them naturally in many foods. When you consume aspartame, your body breaks it down into these amino acids, just as it would with other proteins.
Head-to-Head Comparison: The Key Differences
While both sweeten your food without sugar, their fundamental differences impact how you use them and how your body handles them.
Chemical Structure & Stability
The biggest practical difference comes from their stability. Sucralose is heat-stable, meaning it holds up well in the oven. This makes it a go-to choice for baking sugar-free cookies, cakes, and other treats.
Aspartame, on the other hand, is not heat-stable. When heated, it loses its sweetness. This is why you’ll find it in products like diet sodas and sugar-free yogurt, but not in baked goods.
Sweetness and Taste Profile
Both are intensely sweet, but sucralose is about three times sweeter than aspartame. In terms of taste, this is subjective. Many people find aspartame’s taste to be cleaner and closer to actual sugar. However, some are sensitive to a distinct aftertaste with both. The best way to know which you prefer is simply to try them.
How They Are Metabolized
Your body treats these two sweeteners very differently. The vast majority of sucralose passes through your digestive system unabsorbed.
Aspartame is fully broken down by the body into its constituent amino acids. This is a key point of contention in safety debates, but for most people, it’s a perfectly normal metabolic process. The one major exception is for individuals with a rare genetic disorder called phenylketonuria (PKU). These individuals cannot metabolize phenylalanine, so they must avoid aspartame completely.
The Health Debate: Safety, Side Effects, and Controversies
This is the most important question for many: are they safe?
Are They Safe? The Scientific Consensus
Despite years of controversy and alarming headlines, the overwhelming scientific and regulatory consensus is that both sucralose and aspartame are safe for human consumption at acceptable daily intake levels. Major global health bodies, including the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) and the World Health Organization (WHO), have extensively reviewed the research and approved their use.
について National Cancer Institute also states that there is no clear evidence that these sweeteners cause cancer in humans.
Common Side Effects and Myths Debunked
While approved as safe, some people report side effects. Some studies suggest that artificial sweeteners may alter the balance of gut bacteria, but more research is needed to understand the long-term implications.
The most critical safety concern relates to aspartame and PKU. This is why all products containing aspartame must carry a warning label for phenylketonurics.
Impact on Specific Health Goals
For Diabetics: Blood Sugar and Insulin Response
For individuals managing diabetes, both sucralose and aspartame are considered safe options. Numerous studies have shown that neither sweetener raises blood sugar or insulin levels, making them effective sugar substitutes for blood glucose control.
For Weight Management
The role of artificial sweeteners in weight management is complex. On one hand, they are a fantastic tool for reducing calorie intake from sugar. Replacing a sugary soda with a diet version can save you over 150 calories.
However, some researchers believe that the intense sweetness without the calories might confuse the body’s response to sugar, potentially affecting appetite. The evidence is mixed, but for most people, using them as part of a balanced diet is a reasonable strategy for calorie reduction.
Which One Is Best for Your Needs?
Here’s a simple decision framework:
For Baking and Cooking
The winner is clear: sucralose. Its ability to withstand high temperatures makes it the only suitable option of the two for any recipe that involves heat.
For Beverages and Cold Foods
Here, it’s a matter of personal taste. Aspartame is widely used in diet sodas and other cold products. If you prefer its taste profile and don’t have PKU, it’s an excellent choice. If you prefer the taste of sucralose, it works just as well in coffee, tea, smoothies, and yogurt.
Your Top Questions Answered (FAQ)
Is sucralose more “natural” than aspartame?
Not really. Sucralose starts from a sugar molecule but is chemically modified. Aspartame is made from amino acids, which are natural, but it’s created through an artificial process. Neither is truly “natural.”
Can using these sweeteners lead to sugar cravings?
The research is inconclusive. Some people find that they help manage cravings, while others feel they increase them. It likely depends on the individual.
What is the recommended daily intake?
The FDA’s acceptable daily intake (ADI) is very high: 50 mg per kg of body weight for aspartame and 5 mg per kg for sucralose. This is equivalent to dozens of diet sodas or sweetener packets per day—far more than most people would ever consume.
The Bottom Line
So, sucralose vs. aspartame—which should you choose?
There is no single “healthier” option. Both are considered safe by major health organizations. The best choice truly comes down to your specific needs:
- If you’re a baker, sucralose (Splenda) is your only reliable option.
- If you have PKU, you must avoid aspartame (Equal).
- For everything else, it’s a matter of personal preference in taste.
The most sensible approach is to use these sweeteners in moderation as part of a balanced, whole-foods-based diet. They are tools to help you reduce sugar, not a magic bullet. Listen to your body, see how you feel, and choose the one that best fits your lifestyle.